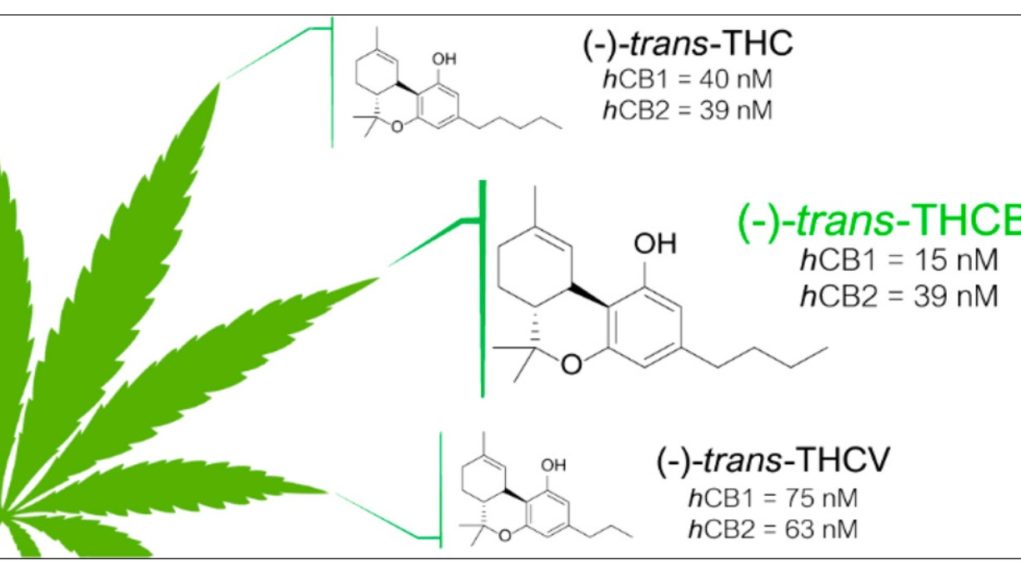
THC-B is a recently discovered novel cannabinoid, also referred to as Delta 9 Tetrahydrocannabutol which is structurally similar to Delta-9 Tetrahydrocannabinol.
What is interesting to note is that THC-B is functionally similar to regular THC, as it binds with both the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors in the brain, although THC-B may be able to better bind with the CB1 receptors in the brain, therefore meaning that its interaction with our endocannabinoid system is higher than with regular THC.
One of the biggest differences between THC-B and regular THC is that instead of having a pentyl side chain, it has a butyl side chain, or in simplest terms, it has one less carbon chain than regular THC.
Another one of the biggest differences here is that THC-B is fully hemp-derived, coming only from the hemp plant, which means that according to the 2018 Farm Bill in the USA it should be 100% legal to purchase and sell at a federal level. Regular THC that comes from cannabis plants is not federally legal.
Now that you have a basic scientific explanation of what THC-B is, let’s move on and figure out what this actually means in terms of human consumption.